Challenges and Opportunities for Electric Aviation


A review published in a recent issue of the Transportation Engineering journal discusses the challenges of sustainable aviation and the technological advancements that are necessary to make electric aviation a viable option. (Photo: Airbus)
As the aviation industry continues to grow, emissions related to aviation also increase. Working towards net zero emissions is a key objective for the industry, and part of that is research and development in electrifying aviation. A review published in a recent issue of the Transportation Engineering journal discusses the challenges of sustainable aviation and the technological advancements that are necessary to make electric aircraft a viable option.
The review, titled “Electric aviation: A review of concepts and enabling technologies,” was sponsored by the Arctic Center for Sustainable Energy through The Arctic University of Norway. Authors Bright Appiah Adu-Gyamfi and Clara Good purport that disruptive innovation is necessary to achieve the industry’s sustainability goals.
The key highlights of the review include the following:
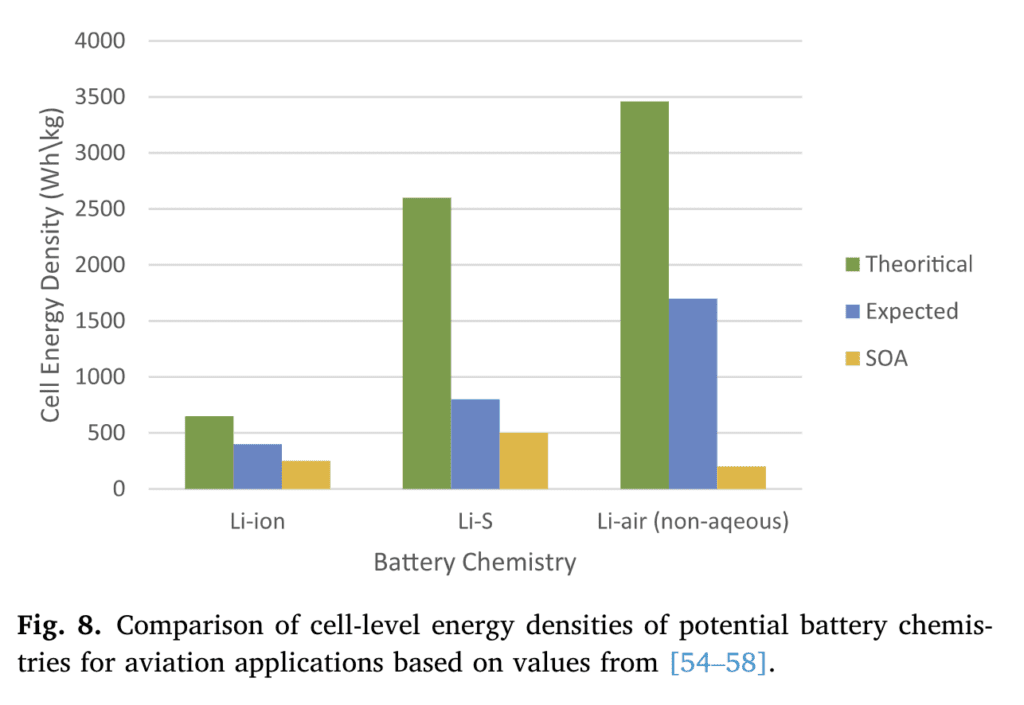
- Battery technology has not achieved sufficient maturity to make commercial electric air transport viable.
- The future of electric aviation will be characterized not only by advancement in battery technology but electric motor technology as well as efficient aerodynamic design.
- Turbo-electric aircraft architecture may present the first opportunity for commercial electric air transport.
In their article, Adu-Gyamfi and Good establish the need for decarbonization and for advancements in aviation technology. They draw attention to the opportunities presented by different electric propulsion architectures, including turbo-electric and hybrid-electric configurations, as well as fully-electric aircraft. Next, the review features a comparative analysis to identify what areas of development are critical to enable electric aviation. Adu-Gyamfi and Good also cover some of the current concepts for electric aircraft and what technologies have the potential to be implemented in the relative short-term.
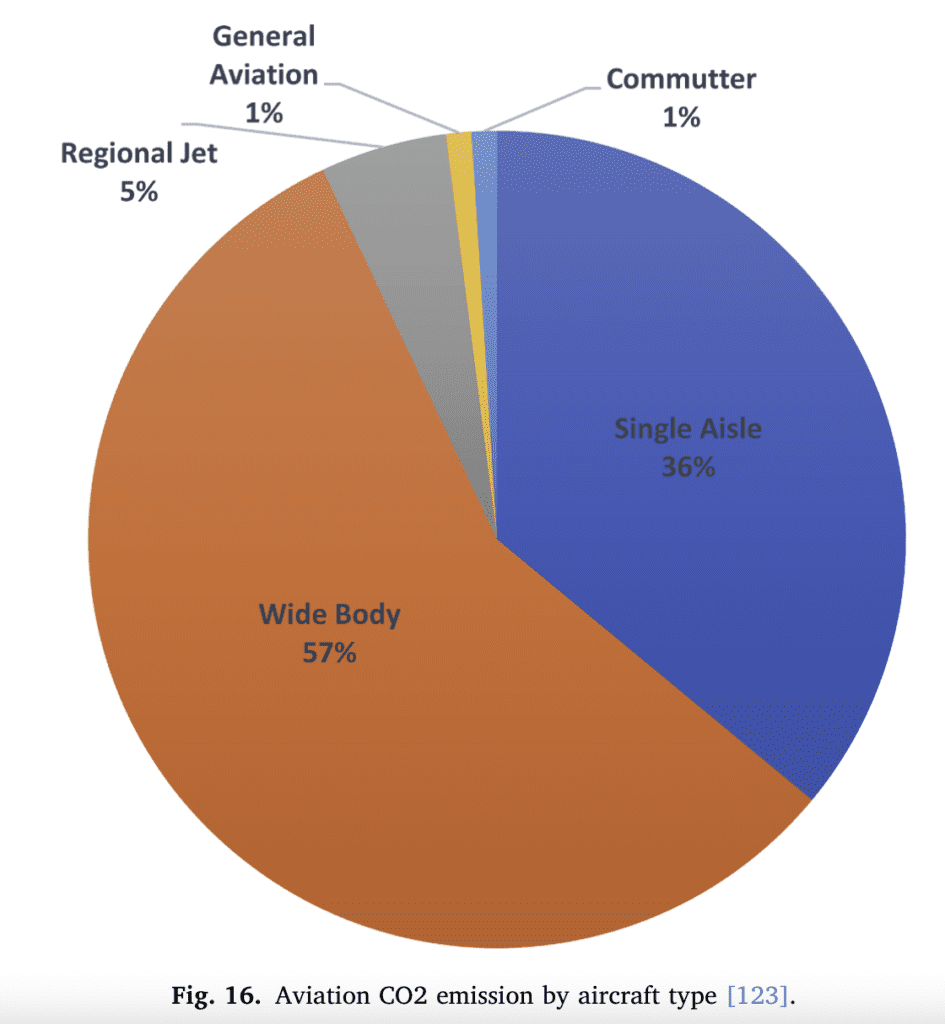
(Graph from article by Bright Appiah Adu-Gyamfi and Clara Good published in Transportation Engineering Volume 9, September 2022)
One of the main factors preventing developments in electric aviation is the low energy density of today’s battery technology, which limits the maximum range of aircraft. “To match the electrical energy equivalent required to power an Airbus A320 using present technology, the batteries’ weight will exceed the maximum take-off weight by a factor of 38,” write Adu-Gyamfi and Good.
They explain that, while current battery technology is limited, distributed propulsion may have the potential to enable more powerful electric aircraft. “The two most common distributed propulsion techniques used are Distributed electric propulsion (DEP) and Turbo-electric distributed propulsion (TeDP),” the review states.
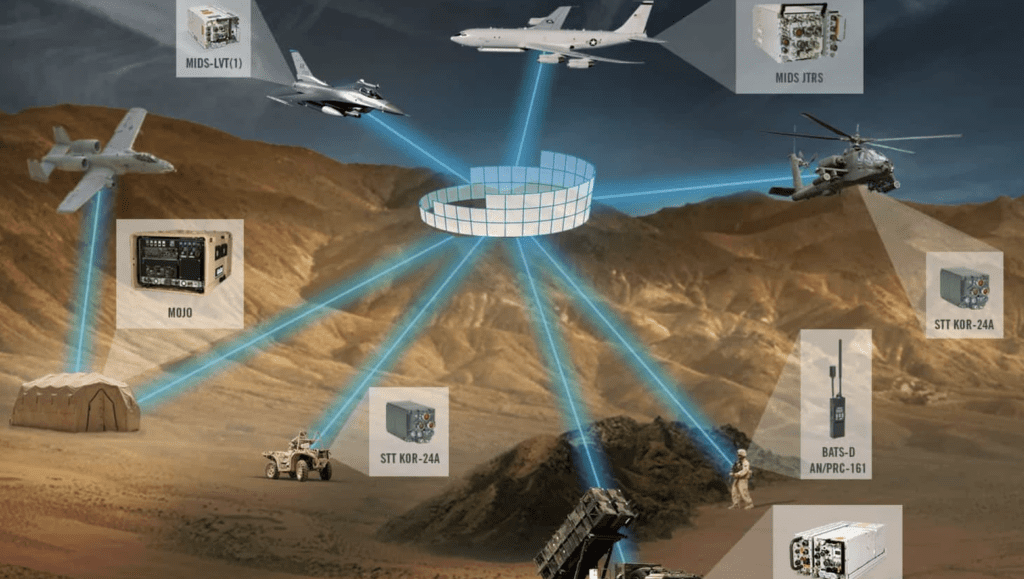
(Figure from article by Bright Appiah Adu-Gyamfi and Clara Good published in Transportation Engineering Volume 9, September 2022)
Fully electric or hybrid-electric propulsion may be more practical for small aircraft that are designed to travel 500 km or less at a time. However, to make a significant reduction in emissions, larger aircraft also need to be electrified. Single-aisle and regional fleets contribute to 41% of the industry’s emissions.
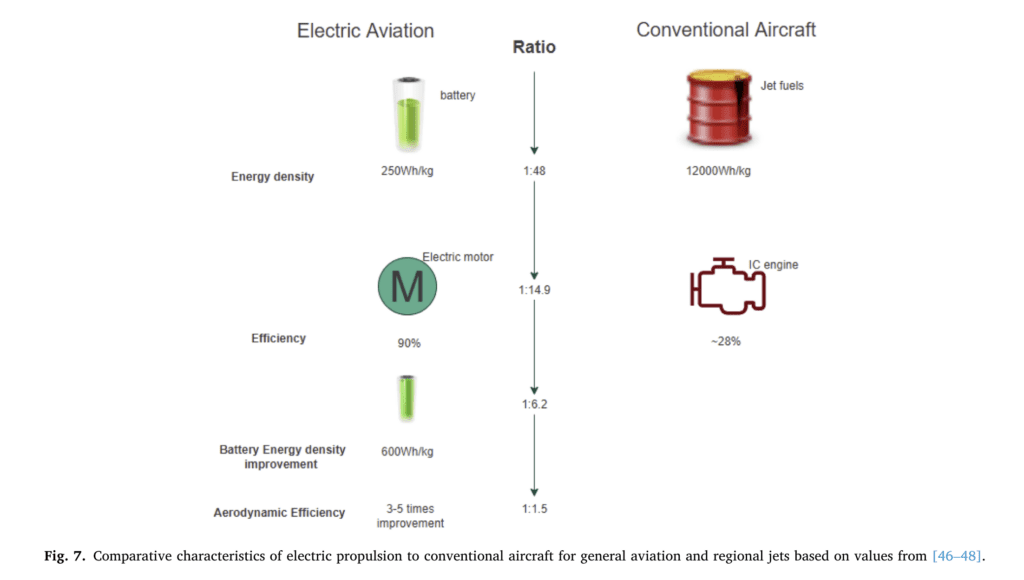
(Figure from article by Bright Appiah Adu-Gyamfi and Clara Good published in Transportation Engineering Volume 9, September 2022)
The authors of the review conclude, “Turboelectric aircraft could open the opportunity for the first electric commercial air transport capable of achieving significant emission reduction since the major technological risk of low energy density batteries is eliminated.
“Although other challenges, including power conversion and distribution, low power generators, and issues with power management, still exist, these components are also available in both full-electric and HEP architectures.”
The post Challenges and Opportunities for Electric Aviation appeared first on Avionics International.
—————
Boost Internet Speed–
Free Business Hosting–
Free Email Account–
Dropcatch–
Free Secure Email–
Secure Email–
Cheap VOIP Calls–
Free Hosting–
Boost Inflight Wifi–
Premium Domains–
Free Domains